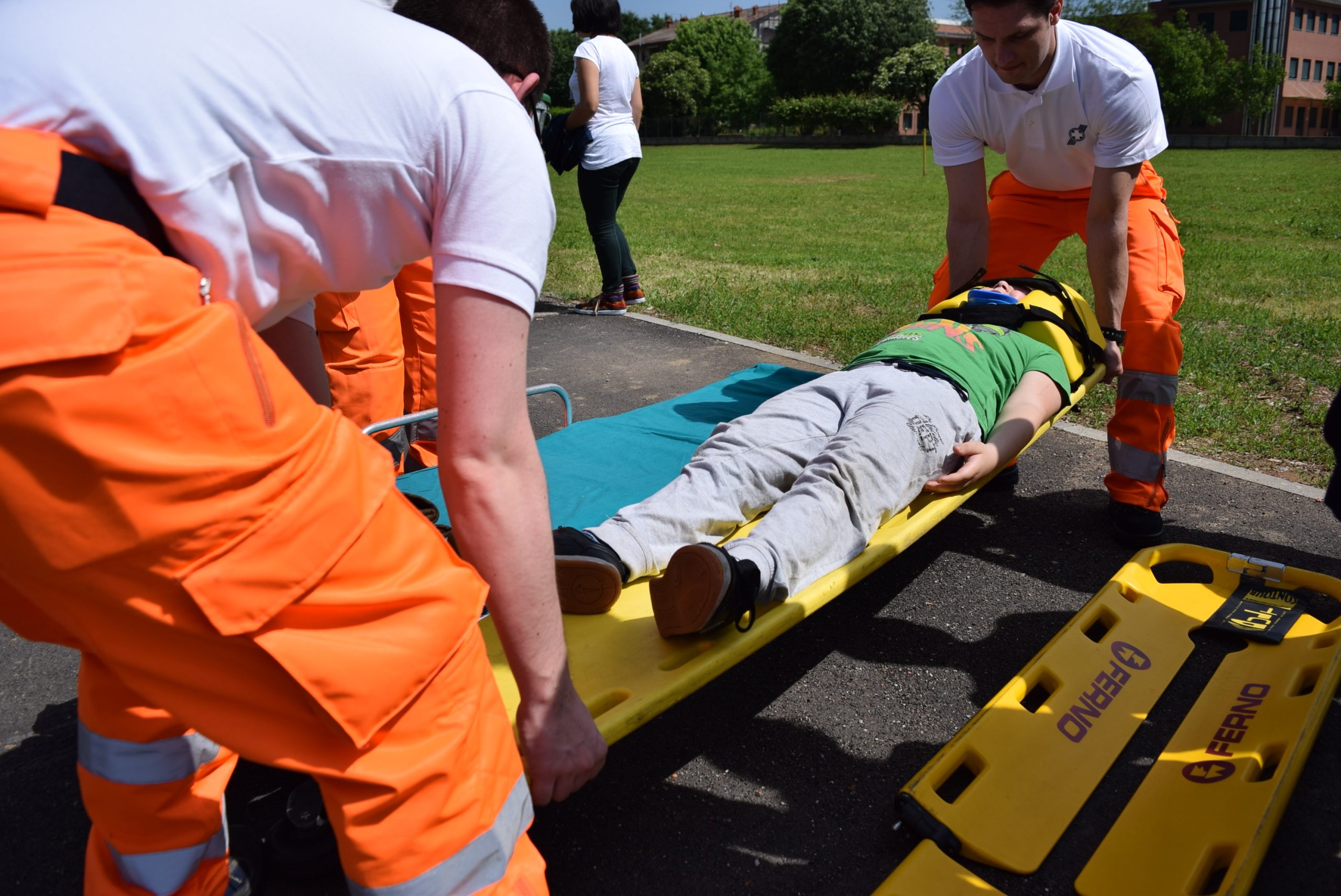
 If you are injured on the job, it is best practice to inform your employer and supervisor about your injuries. They will likely inform you about possible workers’ compensation to which you might be entitled. Are you still eligible to receive workers’ compensation benefits if you tried to hide your injury from your employer?
If you are injured on the job, it is best practice to inform your employer and supervisor about your injuries. They will likely inform you about possible workers’ compensation to which you might be entitled. Are you still eligible to receive workers’ compensation benefits if you tried to hide your injury from your employer?
Gary Jeansonne worked as a maintenance worker at a youth center located in Bunkie, Louisiana. Over two months after Jeansonne stopped working at the center, he filed a claim for workers’ compensation, claiming he had hurt his back while working at the center. He claimed the accident had occurred while he was working in the kitchen. Jeansonne claimed to have called his supervisor the next morning to tell him he would not be able to come in to work due to his back, but he did not tell his supervisor his back issues were from an injury at work.
Jeansonne started receiving medical treatment for his back injuries. His medical records indicate he told his doctor the accident that hurt his back occurred at home. Jeansonne subsequently claimed the report was not accurate and he had just said the incident occurred at home because he wanted to be able to go back to work.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog


 If you are in a car accident and your insurance pays your claim, you likely expect the same thing will happen if you are subsequently in a similar accident. What happens if your insurer paid your prior claim, but tries to deny a subsequent claim?
If you are in a car accident and your insurance pays your claim, you likely expect the same thing will happen if you are subsequently in a similar accident. What happens if your insurer paid your prior claim, but tries to deny a subsequent claim?  A settlement agreement can be an efficient way of resolving a claim and receiving compensation without a lengthy trial process. However, it is essential to understand what a settlement agreement does and does not cover to avoid surprises down the road if you later try to bring related lawsuits against other parties.
A settlement agreement can be an efficient way of resolving a claim and receiving compensation without a lengthy trial process. However, it is essential to understand what a settlement agreement does and does not cover to avoid surprises down the road if you later try to bring related lawsuits against other parties.  Over a decade after Hurricane Katrina, we have almost all heard of the difficult choices hospitals faced while trying to care for patients. This case involves a patient who was allegedly injured while being evacuated from a New Orleans hospital during Hurricane Katrina.
Over a decade after Hurricane Katrina, we have almost all heard of the difficult choices hospitals faced while trying to care for patients. This case involves a patient who was allegedly injured while being evacuated from a New Orleans hospital during Hurricane Katrina.  Even while an inmate, you are still entitled to damages if you are injured on the job. If you are injured while working in a release program, are you entitled to compensation through the workers’ compensation scheme?
Even while an inmate, you are still entitled to damages if you are injured on the job. If you are injured while working in a release program, are you entitled to compensation through the workers’ compensation scheme?  Under Louisiana law, there is a presumption the driver of a car that rear-ends another car acted negligently. However, this presumption of negligence can be overcome in certain situations, such as if the driver of the vehicle that was rear-end shifted lanes soon before the accident.
Under Louisiana law, there is a presumption the driver of a car that rear-ends another car acted negligently. However, this presumption of negligence can be overcome in certain situations, such as if the driver of the vehicle that was rear-end shifted lanes soon before the accident. The distinction between independent contractors and employees has always been something of a balancing test. This distinction becomes vital in workers’ compensation issues, where employees generally enjoy peace of mind with workers’ compensation in the event of an injury, whereas independent contractors usually do not. But are there some cases where an independent contractor can collect workers’ compensation benefits? The answer to this question is illustrated in the following appeal from the New Orleans Office of Workers’ Compensation.
The distinction between independent contractors and employees has always been something of a balancing test. This distinction becomes vital in workers’ compensation issues, where employees generally enjoy peace of mind with workers’ compensation in the event of an injury, whereas independent contractors usually do not. But are there some cases where an independent contractor can collect workers’ compensation benefits? The answer to this question is illustrated in the following appeal from the New Orleans Office of Workers’ Compensation. Everyone knows someone who has been affected by cancer. Despite being a widespread disease, there is a lot we still do not know about cancer. One area where a lot is still unknown is causation. For example, lung cancer can be caused by a variety of things, including smoking and exposure to radioactive materials. These multiple potential causes can present challenging issues in lawsuits where an individual developed cancer. An medical expert is one possible way to address potential causation issues.
Everyone knows someone who has been affected by cancer. Despite being a widespread disease, there is a lot we still do not know about cancer. One area where a lot is still unknown is causation. For example, lung cancer can be caused by a variety of things, including smoking and exposure to radioactive materials. These multiple potential causes can present challenging issues in lawsuits where an individual developed cancer. An medical expert is one possible way to address potential causation issues.  If you have been injured on the job, you might be entitled to workers’ compensation. In order to receive compensation, there are a number of procedural requirements with which you must comply.
If you have been injured on the job, you might be entitled to workers’ compensation. In order to receive compensation, there are a number of procedural requirements with which you must comply.  In order to recover under a homeowner’s policy, there are many requirements with which you must comply. One common requirement is providing the insurer with requested documentation and undergoing an examination under oath where the insurer can ask questions and gather information relevant to the claim. What happens if a homeowner delays undergoing an examination under oath?
In order to recover under a homeowner’s policy, there are many requirements with which you must comply. One common requirement is providing the insurer with requested documentation and undergoing an examination under oath where the insurer can ask questions and gather information relevant to the claim. What happens if a homeowner delays undergoing an examination under oath?