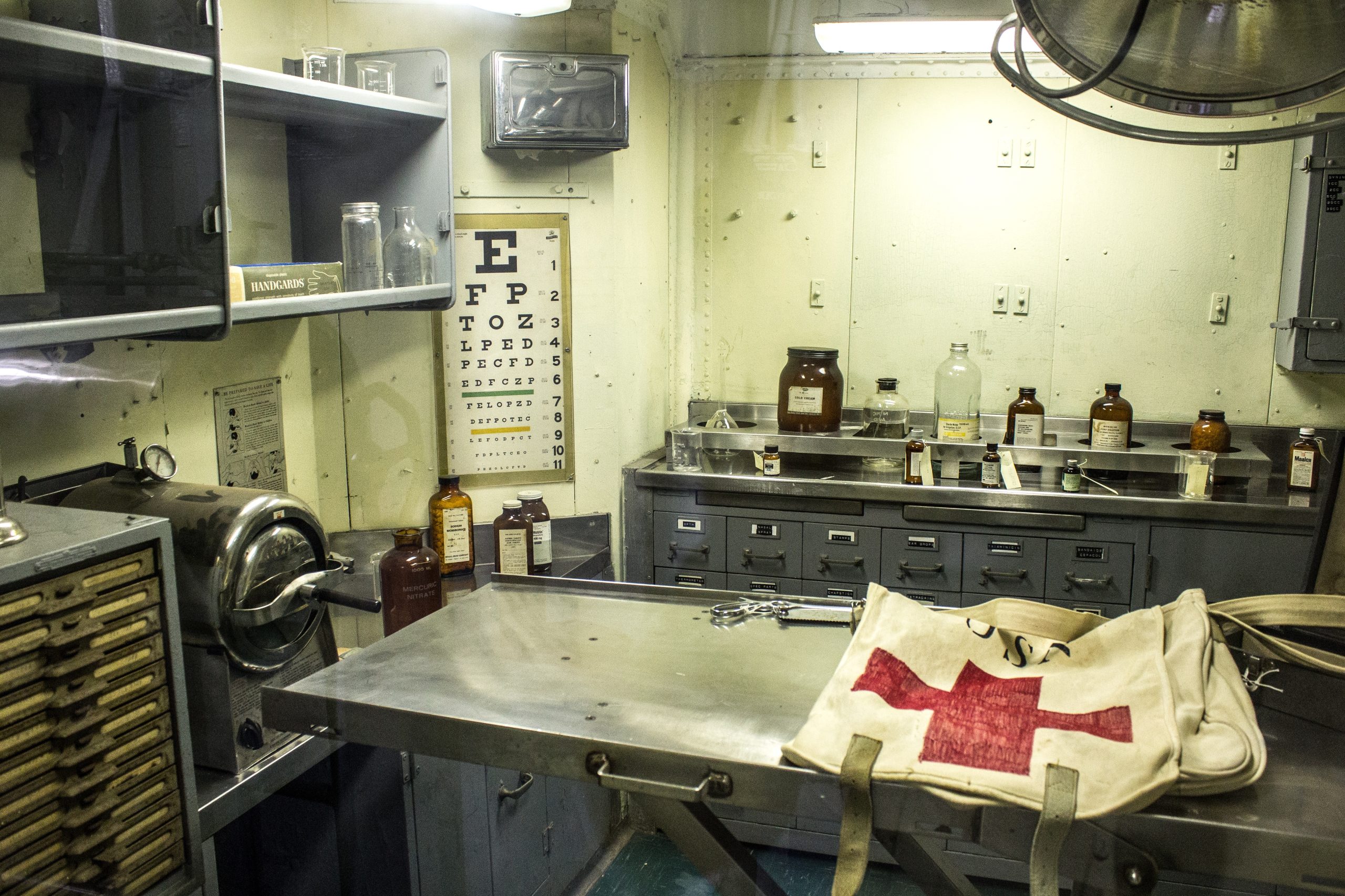
 Medical malpractice claims are not always limited to instances during treatment or surgery and may, as one young patient argued, include failures that occur afterward or post-operatively.
Medical malpractice claims are not always limited to instances during treatment or surgery and may, as one young patient argued, include failures that occur afterward or post-operatively.
Justin Thomas, an eighteen-year-old, aspiring armed serviceman, underwent a right shoulder arthroscopy at Lafayette Surgicare to repair his repeated rotator cuff dislocations. The surgery was considered an outpatient procedure that Thomas’s surgeon, Dr. Otis Drew (Dr. Drew), performed beginning just before 9:00 AM on July 1, 2013, and completed around 11:00 AM the same day. Before and after the surgery, Thomas was given significant anesthesia and medication. By 1:50 PM that afternoon, Thomas was discharged into the care of his parents. Less than six hours later, after Thomas’s mom gave him a prescribed dose of oxycodone, he fell unconscious and was unresponsive to Narcan, so an ambulance arrived at Thomas’ parents’ home taking him back to the hospital, where he lay in a coma for five days. As a result, Thomas experienced brain damage and lost the use of the left side of his body.
In May 2016, a medical review board determined that despite Thomas’s injury, the medical staff, including Dr. Drew, met the required standard of care. Nevertheless, three months later, Thomas filed a lawsuit against Dr. Drew, the anesthesiologist, Lafayette Surgicare, Lafayette Surgery Center, and The Regions Health System of Acadiana. His complaint alleged that he was released too early post-operatively and prescribed extensive anesthesia and heavy narcotic medication that induced him into a coma. In response, Dr. Drew filed a summary judgment motion that the trial court, Fifteenth Judicial District Court Parish of Lafayette, granted, dismissing Thomas’s claims. Thomas appealed to Louisiana’s Third Circuit Court of Appeals (Third Circuit), arguing that the trial court erred in finding that his expert affidavit was inadmissible and did not create a genuine issue of material fact.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog


 The burden of proof lies heavily on claimants to establish the elements of the claim they bring forward. Failing to do so can result in the dismissal of the charge. In the case of George Preston, a prisoner in a Louisiana jail, his complaint against Lieutenant Hicks and four state correctional officers for excessive use of force highlights the importance of meeting the requirements to substantiate a claim. Analyzing the alleged violation of Preston’s Eighth Amendment rights, the court carefully considered the evidence and ultimately decided to dismiss some claims while allowing others to proceed.
The burden of proof lies heavily on claimants to establish the elements of the claim they bring forward. Failing to do so can result in the dismissal of the charge. In the case of George Preston, a prisoner in a Louisiana jail, his complaint against Lieutenant Hicks and four state correctional officers for excessive use of force highlights the importance of meeting the requirements to substantiate a claim. Analyzing the alleged violation of Preston’s Eighth Amendment rights, the court carefully considered the evidence and ultimately decided to dismiss some claims while allowing others to proceed. Most of us get into contracts, not fully understanding all the ins and outs of what we are signing. Similarly, the multiple provisions that can slither their way into contracts can include things like forum selection clauses which can be easily overlooked. But when a lawsuit erupts, can you argue a provision isn’t applicable? The
Most of us get into contracts, not fully understanding all the ins and outs of what we are signing. Similarly, the multiple provisions that can slither their way into contracts can include things like forum selection clauses which can be easily overlooked. But when a lawsuit erupts, can you argue a provision isn’t applicable? The  Timing. We all know it’s important, but how important is it in the legal field? Properly filing documents, adhering to deadlines, and raising legal issues within specific timeframes can significantly impact the outcome of a case. In the following case, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeal looks to the issue of timeliness in the legal field and whether the cause of actions has matured enough to be “ripe” for judicial determination.
Timing. We all know it’s important, but how important is it in the legal field? Properly filing documents, adhering to deadlines, and raising legal issues within specific timeframes can significantly impact the outcome of a case. In the following case, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeal looks to the issue of timeliness in the legal field and whether the cause of actions has matured enough to be “ripe” for judicial determination.  In the realm of insurance coverage disputes, a recent case has brought attention to the application of policy exclusions and their impact on the availability of coverage. Daphne Richardson Valteau took legal action after her father had been stabbed to death on premises owned by The Terraces Limited Partnership (“The Terraces”). The Terraces was managed by Latter & Blum Property Management, Inc. (“Latter & Blum”), while another company, Patriot Protection Agency, Inc. (“Patriot”), had been handling the security services for The Terraces.
In the realm of insurance coverage disputes, a recent case has brought attention to the application of policy exclusions and their impact on the availability of coverage. Daphne Richardson Valteau took legal action after her father had been stabbed to death on premises owned by The Terraces Limited Partnership (“The Terraces”). The Terraces was managed by Latter & Blum Property Management, Inc. (“Latter & Blum”), while another company, Patriot Protection Agency, Inc. (“Patriot”), had been handling the security services for The Terraces. When a prison official fails to provide necessary medical care to an inmate, legal action may be pursued against the individual. However, claiming deliberate indifference to an inmate’s serious medical needs requires meeting specific criteria. As exemplified by the case below, these factors are crucial in preventing individuals from bringing frivolous claims against government officials, ensuring that legitimate cases receive the attention they deserve.
When a prison official fails to provide necessary medical care to an inmate, legal action may be pursued against the individual. However, claiming deliberate indifference to an inmate’s serious medical needs requires meeting specific criteria. As exemplified by the case below, these factors are crucial in preventing individuals from bringing frivolous claims against government officials, ensuring that legitimate cases receive the attention they deserve. Navigating the intricacies of civil litigation requires strict adherence to procedural rules, as the failure to meet deadlines or follow the correct timeline can result in serious consequences for plaintiffs seeking justice. In the case of Michael Neal Rollins, an inmate who filed a lawsuit against the State of Louisiana, Louis Ackal, Sheriff of Iberia Parish, and the Corrections Corporation of America, the impact of missed deadlines and abandoned filings became evident. Rollins alleged physical abuse during his transportation back to the Iberia Parish Jail, but his case was ultimately dismissed due to abandonment. This instance highlights the critical importance of timely and diligent filings within the legal system, emphasizing the need for plaintiffs to navigate the complex procedural landscape to have their claims heard.
Navigating the intricacies of civil litigation requires strict adherence to procedural rules, as the failure to meet deadlines or follow the correct timeline can result in serious consequences for plaintiffs seeking justice. In the case of Michael Neal Rollins, an inmate who filed a lawsuit against the State of Louisiana, Louis Ackal, Sheriff of Iberia Parish, and the Corrections Corporation of America, the impact of missed deadlines and abandoned filings became evident. Rollins alleged physical abuse during his transportation back to the Iberia Parish Jail, but his case was ultimately dismissed due to abandonment. This instance highlights the critical importance of timely and diligent filings within the legal system, emphasizing the need for plaintiffs to navigate the complex procedural landscape to have their claims heard. Workplace accidents can strike unexpectedly, leaving individuals injured and grappling with the complex question of who bears responsibility. However, when such accidents involve heavy machinery and contractual relationships, determining fault can become even more challenging. In the case of Clark Nixon, a dump truck driver at Terrebonne Levee & Conservation District (TLCD), the lines blurred further when an incident unfolded on the job site. As Nixon seeks justice for his injuries, the lawsuit shines a light on the intricate interplay of liability, contractual obligations, and the need for skilled legal representation to recover medical costs and hold those at fault accountable.
Workplace accidents can strike unexpectedly, leaving individuals injured and grappling with the complex question of who bears responsibility. However, when such accidents involve heavy machinery and contractual relationships, determining fault can become even more challenging. In the case of Clark Nixon, a dump truck driver at Terrebonne Levee & Conservation District (TLCD), the lines blurred further when an incident unfolded on the job site. As Nixon seeks justice for his injuries, the lawsuit shines a light on the intricate interplay of liability, contractual obligations, and the need for skilled legal representation to recover medical costs and hold those at fault accountable. The story of an underdog seeking justice against a powerful corporation is a familiar legal narrative. And while we may be inclined to root for the little guy, that does not relieve him from proving he has a valid case.
The story of an underdog seeking justice against a powerful corporation is a familiar legal narrative. And while we may be inclined to root for the little guy, that does not relieve him from proving he has a valid case. When a patient suffers from harm done to them by the negligence of a health care provider, he may be a victim of medical malpractice. A recent Louisiana Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals case explained why it is not always a case of medical malpractice when an avoidable medical death occurs.
When a patient suffers from harm done to them by the negligence of a health care provider, he may be a victim of medical malpractice. A recent Louisiana Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals case explained why it is not always a case of medical malpractice when an avoidable medical death occurs.