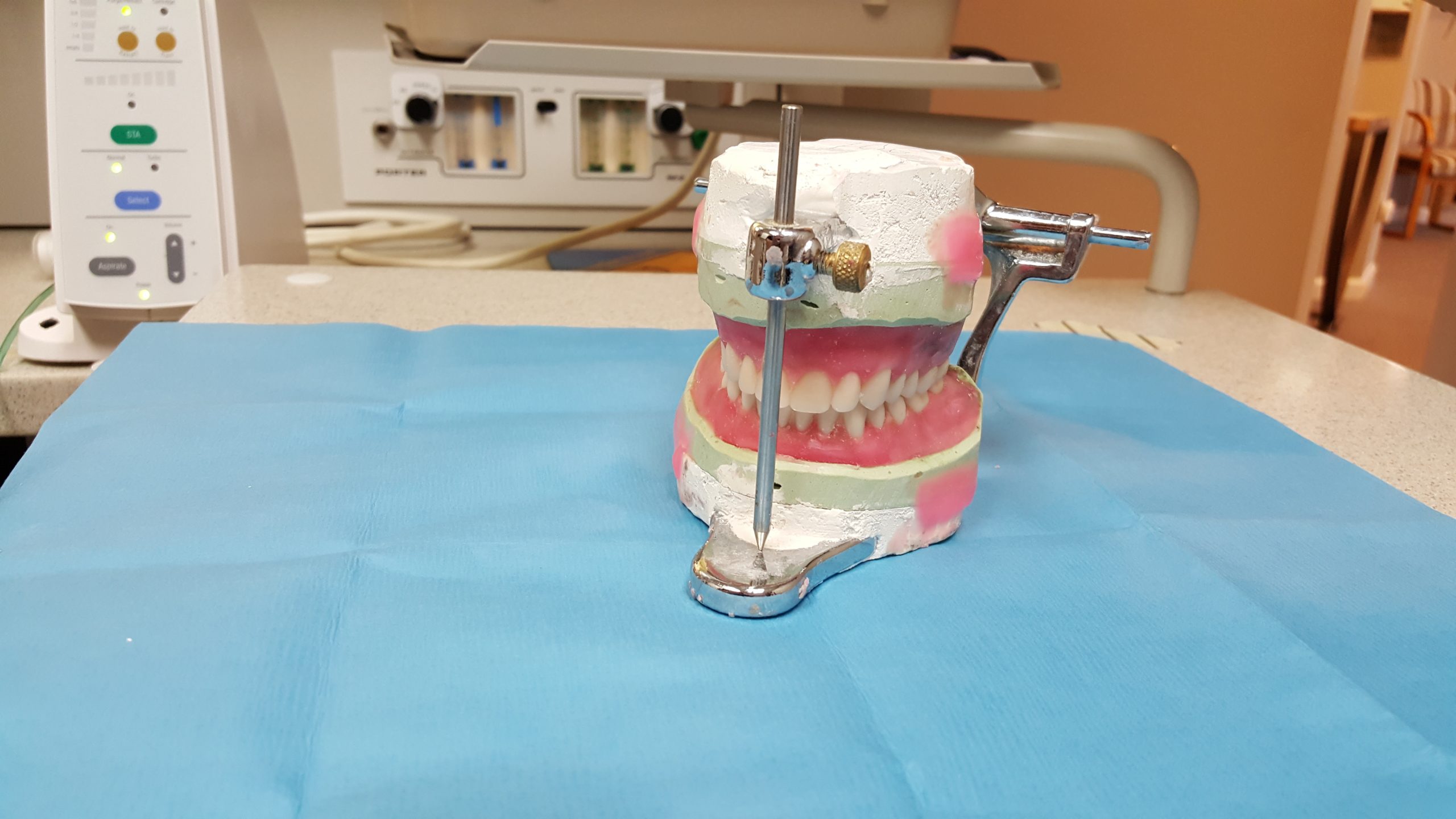
 Appeals from trial court decisions can be costly, especially if the result is again not decided in your favor. Tara Lorraine (“Ms. Lorraine”), a dental patient at Bluebonnet Dental Care, L.L.C., learned this the hard way after appealing a jury verdict decided against her. The Louisiana Court of Appeals for the First Circuit (“First Circuit”) affirmed that jury verdict and assigned costs of the appeal to be paid by Ms. Lorraine. The following case shows the difficulty in proceeding with a medical malpractice lawsuit in Louisiana based on alleged substandard dental procedures.
Appeals from trial court decisions can be costly, especially if the result is again not decided in your favor. Tara Lorraine (“Ms. Lorraine”), a dental patient at Bluebonnet Dental Care, L.L.C., learned this the hard way after appealing a jury verdict decided against her. The Louisiana Court of Appeals for the First Circuit (“First Circuit”) affirmed that jury verdict and assigned costs of the appeal to be paid by Ms. Lorraine. The following case shows the difficulty in proceeding with a medical malpractice lawsuit in Louisiana based on alleged substandard dental procedures.
Ms. Lorraine alleged that her injuries occurred during several dental treatments over several months. First, on January 21, 2010, Ms. Lorraine accused Dr. Ross Quartano (“Dr. Quartano”) of spilling etchant on her throat, which left her with a permanent scar. Then, on April 30, 2010, she accused Dr. Louis Lamendola (“Dr. Lamendola”) of extracting one of her teeth without her consent. Finally, Ms. Lorraine claimed that Dr. Andre Bruni (“Dr. Bruni”) and Dr. Quartano failed to remove substantial underlying decay before they filled some of her teeth, causing her such extreme pain that eventually, she had to seek additional help from a different dentist.
Subsequently, Ms. Lorraine filed a complaint with Louisiana’s Patient Compensation Fund, asking for a medical review panel of each of the three doctors. Upon reviewing Ms. Lorraine’s complaint, the medical review panel found that there was no evidence to support a breach of the standard of care as it related to Dr. Quartano and Dr. Bruni and that a material fact existed regarding Ms. Lorraine’s informed consent with Dr. Lamendola’s removal of her tooth. Thus it did not necessitate an opinion from the medical review panel. However, despite these findings, Ms. Lorraine filed a lawsuit against the same three doctors in the 19th Judicial District Court. Like the medical review panel, the jury found that Ms. Lorraine failed to prove the breach of standards of care. Therefore, the court entered a judgment in favor of the doctors, dismissing Ms. Lorraine’s claims and denying her request for a new trial.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog

 Car accidents are extremely traumatic events that can impact the lives of anyone involved. The legal issues arising after a car accident can be complex and affect everyone involved. For example, what are the rights of a tutor when bringing claims on behalf of the children they are responsible for? Will they be considered “parents” under the law and be allowed to bring a claim for loss of consortium? The following case out of Baton Rouge discusses those issues in relation to a car accident.
Car accidents are extremely traumatic events that can impact the lives of anyone involved. The legal issues arising after a car accident can be complex and affect everyone involved. For example, what are the rights of a tutor when bringing claims on behalf of the children they are responsible for? Will they be considered “parents” under the law and be allowed to bring a claim for loss of consortium? The following case out of Baton Rouge discusses those issues in relation to a car accident.  After a workplace accident, an employee may be flustered, but it is essential that the employee promptly becomes knowledgeable about court requirements and deadlines. If a claim is not filed within an allocated timeline, the claimant may be barred from bringing the claim forward. The following case out of Jefferson Parish shows why, if you’re fax filing a lawsuit, you must follow the rules precisely.
After a workplace accident, an employee may be flustered, but it is essential that the employee promptly becomes knowledgeable about court requirements and deadlines. If a claim is not filed within an allocated timeline, the claimant may be barred from bringing the claim forward. The following case out of Jefferson Parish shows why, if you’re fax filing a lawsuit, you must follow the rules precisely.  Some consider the workplace as their second home. It is a place where one can thrive intellectually and network simultaneously. However, when a workplace becomes hostile or sexually charged, it can make an employee’s life unbearable. Therefore, to bring a successful claim against FMLA and a hostile workplace, a plaintiff must prove all elements under FMLA and show proof the hostile environment affected their well-being.
Some consider the workplace as their second home. It is a place where one can thrive intellectually and network simultaneously. However, when a workplace becomes hostile or sexually charged, it can make an employee’s life unbearable. Therefore, to bring a successful claim against FMLA and a hostile workplace, a plaintiff must prove all elements under FMLA and show proof the hostile environment affected their well-being. While holding the owner responsible for a dog’s behavior is typically the norm, most reasonable people would know not to approach a barking dog in a gated residence. However, Demetrious Frazier found himself at odds with Luke Difulco after being bitten by one of his dogs while performing his work duties at their home. The following lawsuit answers the question; if you approach a barking dog and it bites you, is the owner liable for your injuries?
While holding the owner responsible for a dog’s behavior is typically the norm, most reasonable people would know not to approach a barking dog in a gated residence. However, Demetrious Frazier found himself at odds with Luke Difulco after being bitten by one of his dogs while performing his work duties at their home. The following lawsuit answers the question; if you approach a barking dog and it bites you, is the owner liable for your injuries? Premises liability is an active area of personal injury law, and accidents occurring on public property are no exception. The question often arises, who is liable for a slip and fall on a public sidewalk? In this case, the Louisiana Third Circuit Court of Appeal was asked to determine the premises liability of the town of Lake Arthur for a fall occurring on a public sidewalk built and maintained by this public entity.
Premises liability is an active area of personal injury law, and accidents occurring on public property are no exception. The question often arises, who is liable for a slip and fall on a public sidewalk? In this case, the Louisiana Third Circuit Court of Appeal was asked to determine the premises liability of the town of Lake Arthur for a fall occurring on a public sidewalk built and maintained by this public entity. Everyone can picture a grocery store on a busy day. The aisles are congested, and workers are hurrying to replace products on the sales floor. There may be stocking carts blocking walkways. Who is responsible if a shopper trips over a worker’s cart and injures herself? What about if the worker and the shopper knew the cart was there?
Everyone can picture a grocery store on a busy day. The aisles are congested, and workers are hurrying to replace products on the sales floor. There may be stocking carts blocking walkways. Who is responsible if a shopper trips over a worker’s cart and injures herself? What about if the worker and the shopper knew the cart was there? Everyone wants to emerge victorious after their day in court, but occasionally the jury will refuse to award the judgment you deserve. When a person loses their case at trial, they can appeal it to a higher court. The appeal process allows for a narrow reconsideration of a case to assure that the lower court got to the correct answer; if the appeals court finds that the lower court did not get the correct answer, they can amend the lower court’s judgment, including the calculation of damages.
Everyone wants to emerge victorious after their day in court, but occasionally the jury will refuse to award the judgment you deserve. When a person loses their case at trial, they can appeal it to a higher court. The appeal process allows for a narrow reconsideration of a case to assure that the lower court got to the correct answer; if the appeals court finds that the lower court did not get the correct answer, they can amend the lower court’s judgment, including the calculation of damages.  Timing is an important part of claiming worker’s compensation in Louisiana.
Timing is an important part of claiming worker’s compensation in Louisiana.  Driving poses undeniable risks. However, travelers may need to consider how unsafe a barrier curb may be in certain situations. When is the state liable for these conditions? A case from the St. John Baptist parish considered how the state department of development and transportation was at fault for construction risks that contributed to an accident.
Driving poses undeniable risks. However, travelers may need to consider how unsafe a barrier curb may be in certain situations. When is the state liable for these conditions? A case from the St. John Baptist parish considered how the state department of development and transportation was at fault for construction risks that contributed to an accident.