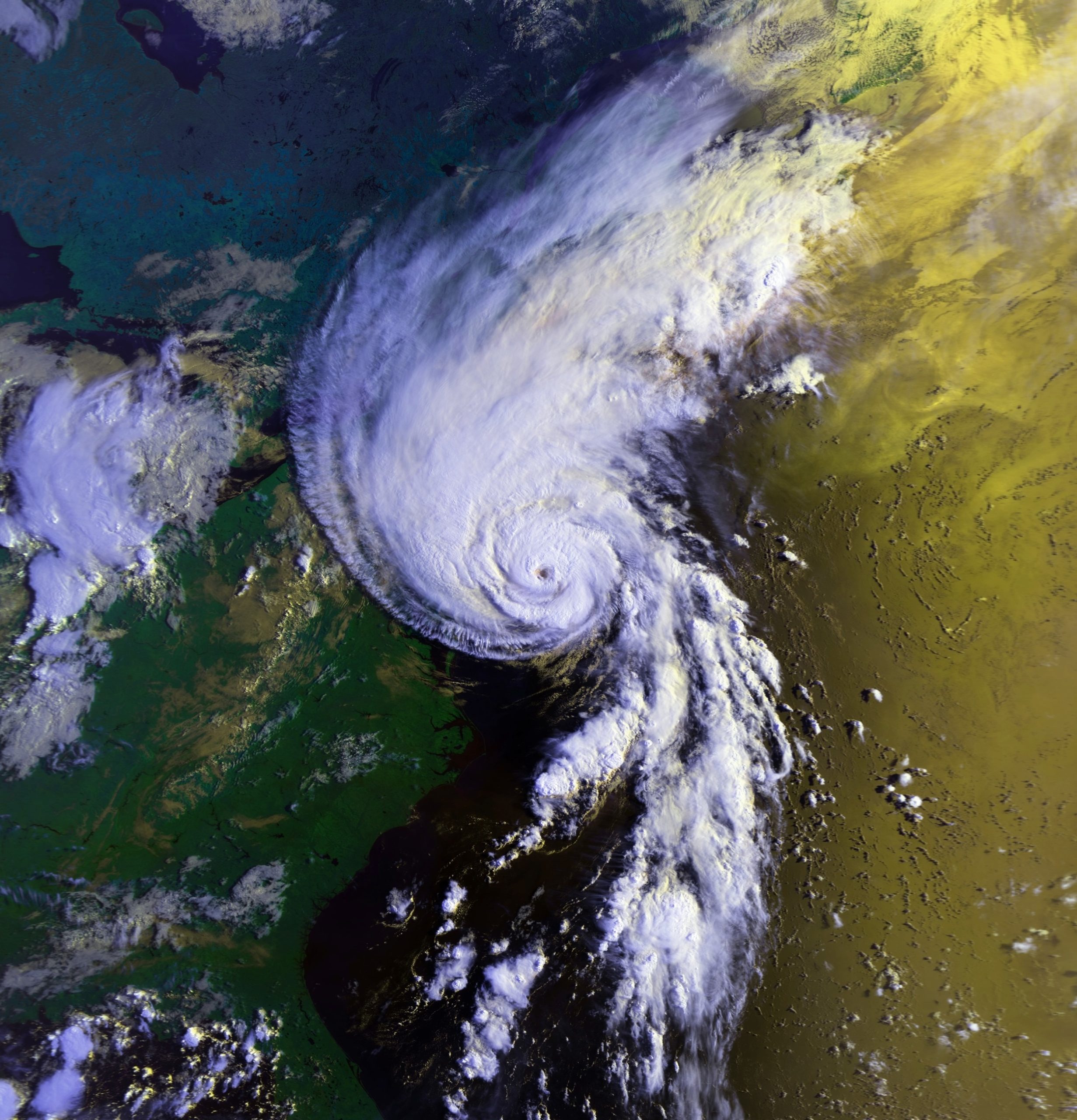
 Over a decade after Hurricane Katrina, we have almost all heard of the difficult choices hospitals faced while trying to care for patients. This case involves a patient who was allegedly injured while being evacuated from a New Orleans hospital during Hurricane Katrina.
Over a decade after Hurricane Katrina, we have almost all heard of the difficult choices hospitals faced while trying to care for patients. This case involves a patient who was allegedly injured while being evacuated from a New Orleans hospital during Hurricane Katrina.
Lionel Favret was admitted to the hospital in New Orleans, Louisiana where he was diagnosed with a bone disease and back pain. He was treated with antibiotics and underwent back surgery. He faced a difficult recover and while in the ICU, Favret had to be resuscitated on two different occasions.
He was moved out of the ICU into a unit for surgery patients when Hurricane Katrina hit. Hospital employees carried Favret down several stories of stairs into the parking garage where he was eventually evacuated after over a day. When he arrived at the new hospital, he was diagnosed with fractures in his back and an infection. He underwent another back surgery.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog


 Dealing with the aftermath of a flood is never fun. This is especially true when the flood damages one of your vehicles. This is the situation Michael Jacobs found himself in after one of his cars was damaged in a flood. After a long fight with his insurance company, he eventually prevailed and was awarded damages.
Dealing with the aftermath of a flood is never fun. This is especially true when the flood damages one of your vehicles. This is the situation Michael Jacobs found himself in after one of his cars was damaged in a flood. After a long fight with his insurance company, he eventually prevailed and was awarded damages.  When you think about medical malpractice lawsuits, a botched surgery or missed diagnosis are likely the first things that come to mind. The following case involves a less common situation involving purported medical malpractice involving physical therapy post-surgery. It analyzes the relationship between a doctor and a physical therapist and whether a doctor can be vicariously liable for the actions of a physical therapist.
When you think about medical malpractice lawsuits, a botched surgery or missed diagnosis are likely the first things that come to mind. The following case involves a less common situation involving purported medical malpractice involving physical therapy post-surgery. It analyzes the relationship between a doctor and a physical therapist and whether a doctor can be vicariously liable for the actions of a physical therapist. It can be challenging to interpret insurance policies, especially when they involve complex provisions such as coverage for an additional insured. Before signing an insurance policy, it is imperative to understand its language and what it does and does not cover. Here, the plain language of the insurance policy proved instrumental in the appellate court’s ruling.
It can be challenging to interpret insurance policies, especially when they involve complex provisions such as coverage for an additional insured. Before signing an insurance policy, it is imperative to understand its language and what it does and does not cover. Here, the plain language of the insurance policy proved instrumental in the appellate court’s ruling. Sometimes, those delightful recreational activities we all enjoy carry an inherent risk. Often, we assume the risk of those injuries when we engage in that potentially reckless conduct. Knowing your legal options following these injuries is necessary, mainly because recovering for these somewhat ordinary injuries can be difficult. What does it look like when a party cannot recover for a recreational injury–here, an injury from a trampoline park visit?
Sometimes, those delightful recreational activities we all enjoy carry an inherent risk. Often, we assume the risk of those injuries when we engage in that potentially reckless conduct. Knowing your legal options following these injuries is necessary, mainly because recovering for these somewhat ordinary injuries can be difficult. What does it look like when a party cannot recover for a recreational injury–here, an injury from a trampoline park visit? Picture this: you’re enjoying your daily dose of local news when your name surfaces amidst a hailstorm of defamatory allegations. Your reputation takes a blow, and you decide to fight back by filing a lawsuit. This might sound like a gripping storyline from a TV courtroom drama, but for Mary R, this was a harsh reality. Today we’ll delve into her case, a fascinating battle highlighting the intriguing intersections between public figures, free speech, and defamation law.
Picture this: you’re enjoying your daily dose of local news when your name surfaces amidst a hailstorm of defamatory allegations. Your reputation takes a blow, and you decide to fight back by filing a lawsuit. This might sound like a gripping storyline from a TV courtroom drama, but for Mary R, this was a harsh reality. Today we’ll delve into her case, a fascinating battle highlighting the intriguing intersections between public figures, free speech, and defamation law. When an injury related to a product occurs, assigning fault can involve multiple parties. In personal injury litigation, crucial legal questions arise regarding whom the plaintiff can seek compensation from, if anyone, and the underlying theory of liability. The following case offers a valuable exploration of common liability theories often encountered in product-related injury cases.
When an injury related to a product occurs, assigning fault can involve multiple parties. In personal injury litigation, crucial legal questions arise regarding whom the plaintiff can seek compensation from, if anyone, and the underlying theory of liability. The following case offers a valuable exploration of common liability theories often encountered in product-related injury cases. Personal attacks often take center stage in the tumultuous arena of modern political campaigns, leaving no stone unturned and no reputation untouched. Yet, amidst this well-trodden path of character assaults, a unique legal battle emerges, where the crosshairs were not directed at a political rival but rather a candidate’s ex-spouse. In a case that blurs the lines between public discourse and private matters, the spotlight falls on the intersection of defamation claims and the exercise of free speech. Can a campaign ad’s accusations against an ex-spouse be enough to launch a successful legal battle?
Personal attacks often take center stage in the tumultuous arena of modern political campaigns, leaving no stone unturned and no reputation untouched. Yet, amidst this well-trodden path of character assaults, a unique legal battle emerges, where the crosshairs were not directed at a political rival but rather a candidate’s ex-spouse. In a case that blurs the lines between public discourse and private matters, the spotlight falls on the intersection of defamation claims and the exercise of free speech. Can a campaign ad’s accusations against an ex-spouse be enough to launch a successful legal battle? Imagine the hardships of being denied basic necessities solely because of a disability. In such cases, how can individuals with disabilities navigate the legal system to seek justice and equal treatment? These questions gain significant relevance when we examine recent allegations of denied accommodations and rights violations. This situation sheds light on the challenges confronted by individuals with disabilities and raises important considerations regarding the responsibility of institutions to provide reasonable accommodations. The pursuit of justice and equal rights is a fundamental principle in any democratic society, yet there are instances where individuals encounter substantial obstacles, particularly in cases involving accessibility rights.
Imagine the hardships of being denied basic necessities solely because of a disability. In such cases, how can individuals with disabilities navigate the legal system to seek justice and equal treatment? These questions gain significant relevance when we examine recent allegations of denied accommodations and rights violations. This situation sheds light on the challenges confronted by individuals with disabilities and raises important considerations regarding the responsibility of institutions to provide reasonable accommodations. The pursuit of justice and equal rights is a fundamental principle in any democratic society, yet there are instances where individuals encounter substantial obstacles, particularly in cases involving accessibility rights. Mistakes are inevitable in human experiences, but some mistakes can have significant legal consequences. Just like regular folks, courts are infallible and make mistakes as well. What happens when a court fails to include all required information in a judgment? Such a failure creates confusion and can impede the appeals process and delay justice for the parties involved, as seen in the following case.
Mistakes are inevitable in human experiences, but some mistakes can have significant legal consequences. Just like regular folks, courts are infallible and make mistakes as well. What happens when a court fails to include all required information in a judgment? Such a failure creates confusion and can impede the appeals process and delay justice for the parties involved, as seen in the following case.