 Sufficient evidence is required to prevail in any lawsuit. Generally, each side obtains additional evidence through the discovery process. However, what happens if a court grants a summary judgment motion for one party before the other party has time to complete adequate discovery? The following case helps answer this question.
Sufficient evidence is required to prevail in any lawsuit. Generally, each side obtains additional evidence through the discovery process. However, what happens if a court grants a summary judgment motion for one party before the other party has time to complete adequate discovery? The following case helps answer this question.
Shannon James Suarez supposedly threw a Twinkie box at Jerry W. Peloquin II. Peloquin claimed Suarez had previously been stalking him for months and battered him. Lori Smith also claimed Suarez had stalked her. Suarez was subsequently arrested and charged with stalking under La. R.S. 14:40.2(A).
The investigator, Bill Pousson, went to Suarez’s workplace to talk to him about the charges. Suarez claims Pousson spoke to him, told him he could make his problems disappear, and encouraged him to plead guilty, even though he knew Suarez had an attorney. Suarez then filed a lawsuit against Pousson and John DeRosier, the district attorney (the “Defendants”), claiming malicious prosecution and misconduct related to the District Attorney’s Office’s investigation.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
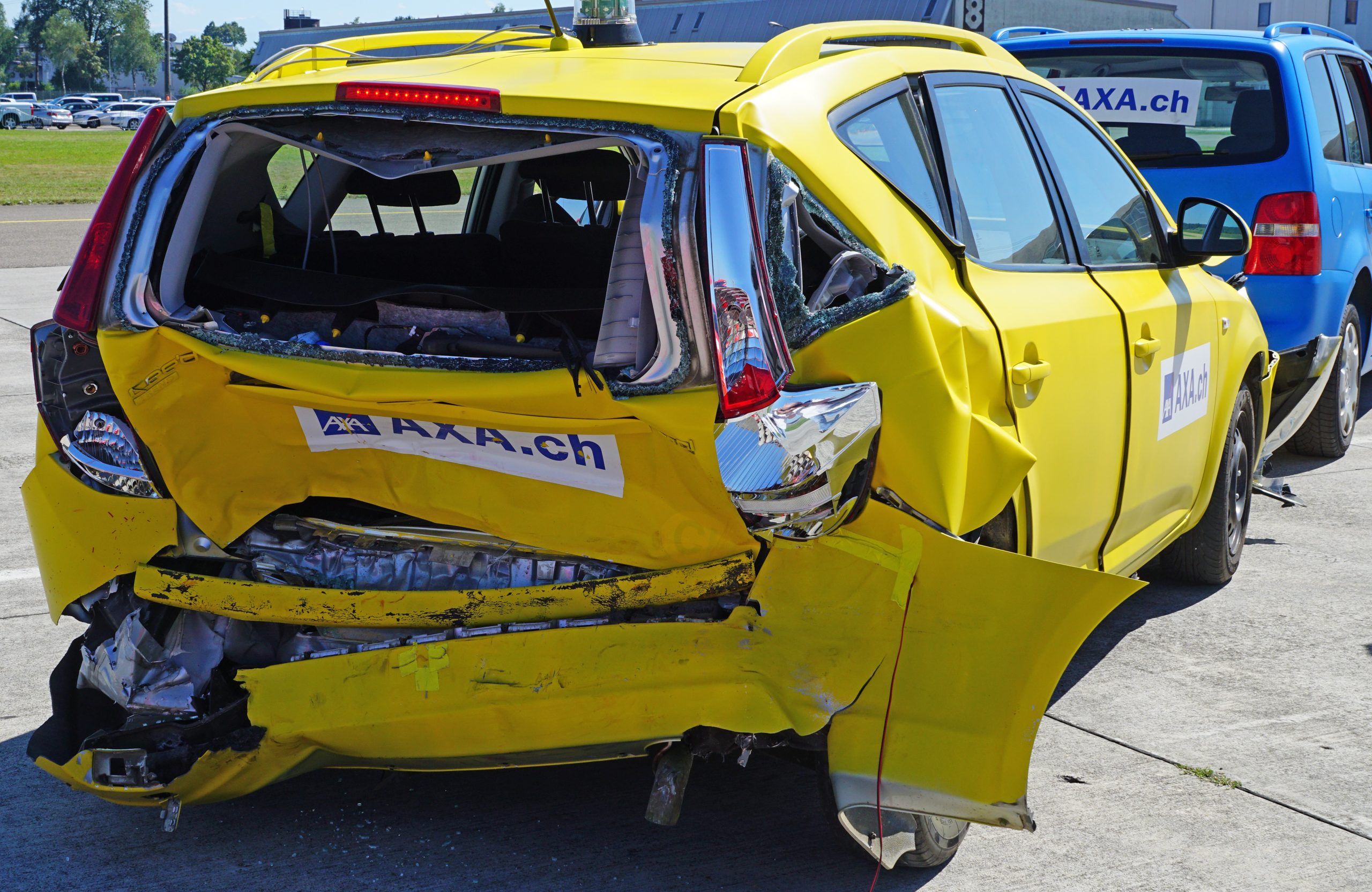

 One of the joys of adulthood is figuring out insurance coverage for your vehicles. Selecting the right coverage can be incredibly challenging when you own a small business because there are unclear lines between personal and company vehicles. This can be especially challenging if an accident occurs when driving a different vehicle than you usually drive. Can your insurance policy cover you when driving a different vehicle because your regular vehicle is out of commission and needs repairs? The subsequent lawsuit helps answer this question.
One of the joys of adulthood is figuring out insurance coverage for your vehicles. Selecting the right coverage can be incredibly challenging when you own a small business because there are unclear lines between personal and company vehicles. This can be especially challenging if an accident occurs when driving a different vehicle than you usually drive. Can your insurance policy cover you when driving a different vehicle because your regular vehicle is out of commission and needs repairs? The subsequent lawsuit helps answer this question. Even if you have a unique job like a stunt performer, you can still get brought down to Earth by the complexities of determining what your insurance policies do and do not cover if you are involved in an insurance coverage dispute. In that case, it is important to understand the plain language of your insurance contract, how different provisions in the policy interact, and how courts interpret insurance policies.
Even if you have a unique job like a stunt performer, you can still get brought down to Earth by the complexities of determining what your insurance policies do and do not cover if you are involved in an insurance coverage dispute. In that case, it is important to understand the plain language of your insurance contract, how different provisions in the policy interact, and how courts interpret insurance policies.  When a loved one dies in a car accident, dealing with insurance is likely the last thing on your mind. Unfortunately, insurance policies can be complicated, with many details and exceptions. If you do not fully understand your insurance coverage, you might find yourself in a difficult situation when seeking compensation from your insurance company. This is especially important when your vehicles and insurance policies cover multiple states.
When a loved one dies in a car accident, dealing with insurance is likely the last thing on your mind. Unfortunately, insurance policies can be complicated, with many details and exceptions. If you do not fully understand your insurance coverage, you might find yourself in a difficult situation when seeking compensation from your insurance company. This is especially important when your vehicles and insurance policies cover multiple states.  Mardi Gras, a time of joyous celebration, took an unexpected turn for a store near a French Quarter hotel when a sprinkler head malfunctioned, resulting in significant water damage. Despite the storeowner’s insurance covering the damages, a lawsuit ensued to determine the hotel’s liability for the losses incurred. This case highlights the complexities of determining responsibility and legal remedies in property damage cases, emphasizing the importance of seeking legal counsel to navigate such situations effectively.
Mardi Gras, a time of joyous celebration, took an unexpected turn for a store near a French Quarter hotel when a sprinkler head malfunctioned, resulting in significant water damage. Despite the storeowner’s insurance covering the damages, a lawsuit ensued to determine the hotel’s liability for the losses incurred. This case highlights the complexities of determining responsibility and legal remedies in property damage cases, emphasizing the importance of seeking legal counsel to navigate such situations effectively. Losing a lawsuit can lead to frustration with your attorney, and you might contemplate pursuing a legal malpractice claim against them. However, it is crucial to comprehend the essential elements required to succeed in such a claim; otherwise, your case may face dismissal. The Klein v. Wynne lawsuit examines the importance of meeting all the requirements to prevail in a legal malpractice lawsuit and highlights the potential consequences of failing to do so.
Losing a lawsuit can lead to frustration with your attorney, and you might contemplate pursuing a legal malpractice claim against them. However, it is crucial to comprehend the essential elements required to succeed in such a claim; otherwise, your case may face dismissal. The Klein v. Wynne lawsuit examines the importance of meeting all the requirements to prevail in a legal malpractice lawsuit and highlights the potential consequences of failing to do so. Nobody likes insurance policies or divorce. Both can be extremely messy and full of legal jargon. Megan Daigle experienced this firsthand as her divorced parents’ insurance did not cover everything they hoped for.
Nobody likes insurance policies or divorce. Both can be extremely messy and full of legal jargon. Megan Daigle experienced this firsthand as her divorced parents’ insurance did not cover everything they hoped for.  Courts often rely on motions for summary judgments to avoid the costly and time-consuming reality of going to trial and presenting a case in front of a jury. Motions for summary judgment are when one party asks the court to decide the case based on the current facts alleged in their favor. Courts should grant these motions when there are no facts in dispute for the jury to resolve. But how much evidence does a party have to present to survive one of these motions? A case out of New Orleans shows that, in some cases, just having medical records could be enough to deny a motion for summary judgment.
Courts often rely on motions for summary judgments to avoid the costly and time-consuming reality of going to trial and presenting a case in front of a jury. Motions for summary judgment are when one party asks the court to decide the case based on the current facts alleged in their favor. Courts should grant these motions when there are no facts in dispute for the jury to resolve. But how much evidence does a party have to present to survive one of these motions? A case out of New Orleans shows that, in some cases, just having medical records could be enough to deny a motion for summary judgment.  Court cases are contentious, polarizing atmospheres between the parties. Stubbornness is ripe, and the opposing parties are staunchly in, unsurprisingly, opposition. However, sometimes even opposing parties can agree. Any party can take issue with a court’s judgment, and sometimes ALL parties can take issue with a court’s decision–even if these issues are different. But when multiple parties raise various errors in a trial court judgment, how can the higher courts resolve such allegations of error?
Court cases are contentious, polarizing atmospheres between the parties. Stubbornness is ripe, and the opposing parties are staunchly in, unsurprisingly, opposition. However, sometimes even opposing parties can agree. Any party can take issue with a court’s judgment, and sometimes ALL parties can take issue with a court’s decision–even if these issues are different. But when multiple parties raise various errors in a trial court judgment, how can the higher courts resolve such allegations of error?